5.1. TopsIDEAS gcu mix_precision¶
描述¶
用于自动或手动调整topsinference混合精度时每个op的计算精度。
自动混精功能,用户可给定模型输入和输出等,自动找出哪些op需要用fp32计算。 手动混精功能,打开topsinference的统计开关,使用fp32和fp16分别进行一次推理,对比每个op的输出,给出逐元素比较结果和余弦相似度比较结果,用户可以通过这些信息自行判断哪些op需要用fp32计算。
注:使用本功能找到的混精方案(需要设置为fp32计算的op id)只在当前版本topsinference上有效,当变更topsinference版本时,需要重新验证或者重新调整。
命令行¶
准备¶
准备需要校准fp16混精计算的onnx,特指使用topsinference fp32计算结果精度正常而使用默认的fp16混精方案计算精度有损失的onnx。
准备一些真实样本,方法:将推理部署时,经过前处理的数据,保存成npz格式,npz中以模型每个输入的名称作为key,输入数据的ndarray作为value。npz文件必须命名为sample{id}_inputs.npz,如sample0_inputs.npz。对于自动混精功能的命令行使用方式,也需要将golden输出(如cpu fp32计算结果)也保存成同格式、名称对应的npz文件,如sample0_outputs.npz。
准备一个workspace文件夹,校准过程中产生的中间文件会保存在workspace中,对同一个onnx文件、同一个编译设置的多步校准可以复用workspace,节省部分编译时间和空间占用,否则应清空workspace。
使用方法¶
usage: topsideas gcu mix_precision [-h] [--manual] --input_onnx INPUT_ONNX --sample_dir SAMPLE_DIR --workspace WORKSPACE [--clean] [--output_json OUTPUT_JSON]
[--fp32_nodes [FP32_NODES ...]] [--finalize] [--compile_options COMPILE_OPTIONS] [--resource_mode RESOURCE_MODE]
[--min_shapes [MIN_SHAPES ...]] [--max_shapes [MAX_SHAPES ...]] [--device DEVICE] [--cluster [CLUSTER ...]]
[--mode {RAW,CALC}] [--rtol RTOL] [--atol ATOL] [--ntol NTOL] [--cos_sim COS_SIM] [--le_value_thres LE_VALUE_THRES]
[--ge_value_thres GE_VALUE_THRES] [--op_id_filter [OP_ID_FILTER ...] | --op_id_bypass [OP_ID_BYPASS ...] | --op_type_filter
[OP_TYPE_FILTER ...] | --op_type_bypass [OP_TYPE_BYPASS ...]]
参数¶
short |
long |
default |
help |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
show this help message and exit |
|
|
Auto or manual mode, default is auto mode |
||
|
|
Onnx path |
|
|
|
Directory containing sampleN_inputs/outputs.npz |
|
|
|
Set a workspace path to save intermediate results and inter-run cache |
|
|
Clean the workspace |
||
|
|
Report json path |
|
|
|
Set op ids to fp32 precision. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
Enable this to generate executable for deployment. This will cancel the compile options used to compare statistic op results, and disable op outputs statistic feature. Only effective when enable --manual |
Compile Arguments
short |
long |
default |
help |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
TopsInference compile options, json format, see TopsInference docs for more info |
|
|
|
TopsInference compile option, overwrite setting in --compile_options |
|
|
|
Min input shapes. Format: --min_shapes NAME:SHAPE. For example: --min_shapes input1:[1,3,224,224] input2:[1,3,224,224] |
|
|
|
Max input shapes. Format: --max_shapes NAME:SHAPE. For example: --max_shapes input1:[1,3,224,224] input2:[1,3,224,224] |
Run Arguments
short |
long |
default |
help |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Device id |
|
|
|
Cluster ids |
Statistic Arguments
short |
long |
default |
help |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Statistic mode: CALC mode use topsinference built-in feature to statistic op outputs in fp32 and fp16-mix runs separately , including ratio of value exceed defined threshold (default and usually set as fp16 min max value) and Nan; RAW mode use topsinference to dump op-level raw data and do extending statistics mainly between fp32 and fp16-mix runs, including number of Nan/Inf, numpy allclose, cos similarity, and vector norm (length) relative ratio. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Relative tolerance |
|
|
|
Absolute tolerance |
|
|
|
Mismatch number tolerance, eg. ntol=0.01 means 1%% mismatch is allowed. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Use cosine similarity instead of numerical tolerance. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Statistic value number less or equal than thres. Only effective when enable --manual and --mode=CALC |
|
|
|
Statistic value number greater or equal than thres. Only effective when enable --manual and --mode=CALC |
|
|
|
Only statistic specific op ids. Conflict with other filter/bypass options. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Statistic skip specific op ids. Conflict with other filter/bypass options. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Only statistic specific op types. Conflict with other filter/bypass options. Only effective when enable --manual |
|
|
|
Statistic skip specific op types. Conflict with other filter/bypass options. Only effective when enable --manual |
示例1 自动混精¶
命令行方式默认使用自动混精方式。
以lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx为例,准备好真实样本存放到lprnet-samples文件夹,准备一个空文件夹workspace。
步骤1. 以自动方式运行混精校准功能
topsideas gcu mix_precision --input_onnx lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx --sample_dir ./lprnet-samples/ --workspace=./workspace --output_json result.json
自动混精工具查找出设置62号和63号节点后,精度达标。
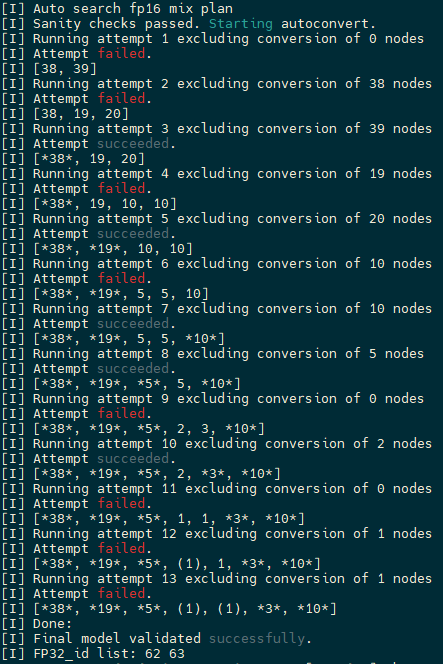
图 5.1.1 自动混精搜索结果¶
步骤2. 产生可用于部署的executable
参考示例2中步骤4。
示例2 手动混精¶
手动混精需要增加--manual参数。
以lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx为例,准备好真实样本存放到lprnet-samples文件夹,准备一个空文件夹workspace。
步骤1. 先运行一次混精校准功能,使用CALC模式
topsideas gcu mix_precision --input_onnx lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx --manual --sample_dir ./lprnet-samples/ --workspace=./workspace --output_json result.json --mode=CALC
整网fp16 fail,fp32 pass:
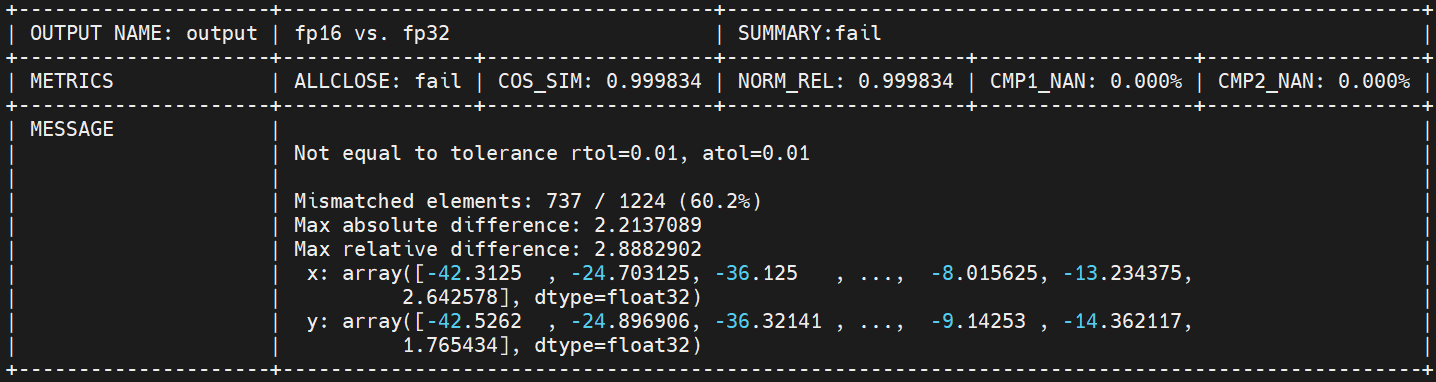
图 5.1.2 步骤1整网结果¶
所有节点中,没有nan,有且只有62号出现上溢出:
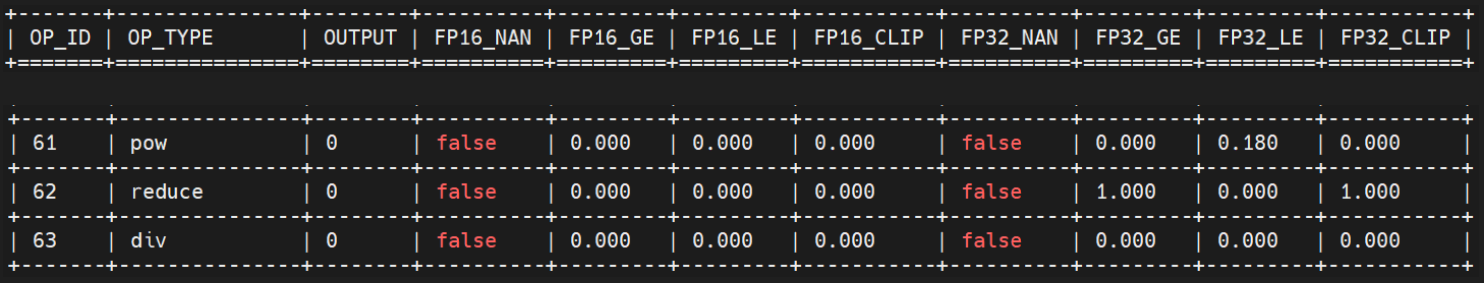
图 5.1.3 步骤1详细结果¶
步骤2. 将62号设为fp32,再运行一次
topsideas gcu mix_precision --input_onnx lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx --manual --sample_dir ./lprnet-samples/ --workspace=./workspace --output_json result.json --mode=CALC --fp32_nodes 62
整网fp16 fail,fp32 pass:
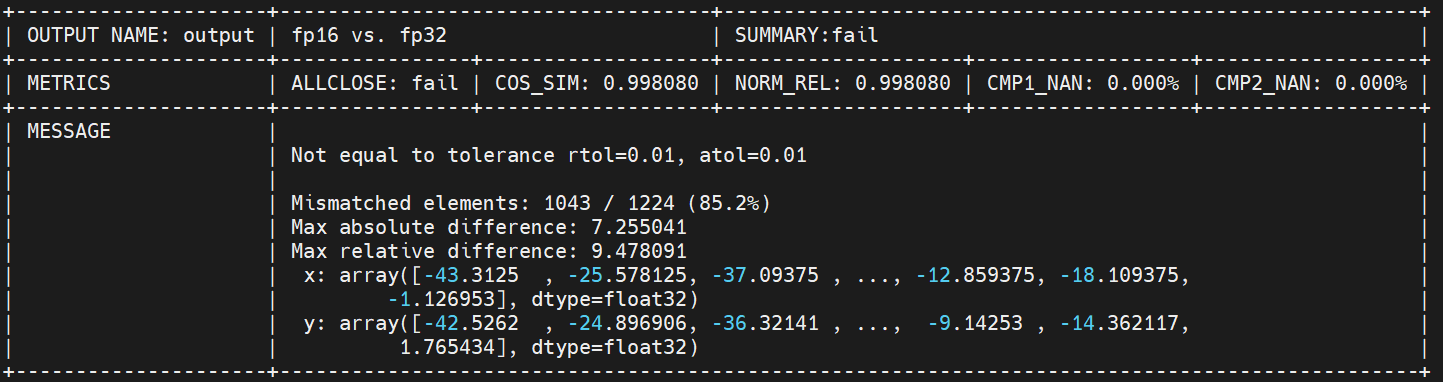
图 5.1.4 步骤2整网结果¶
所有节点中,没有nan,除了已经设为fp32的62号,63也出现上溢出:
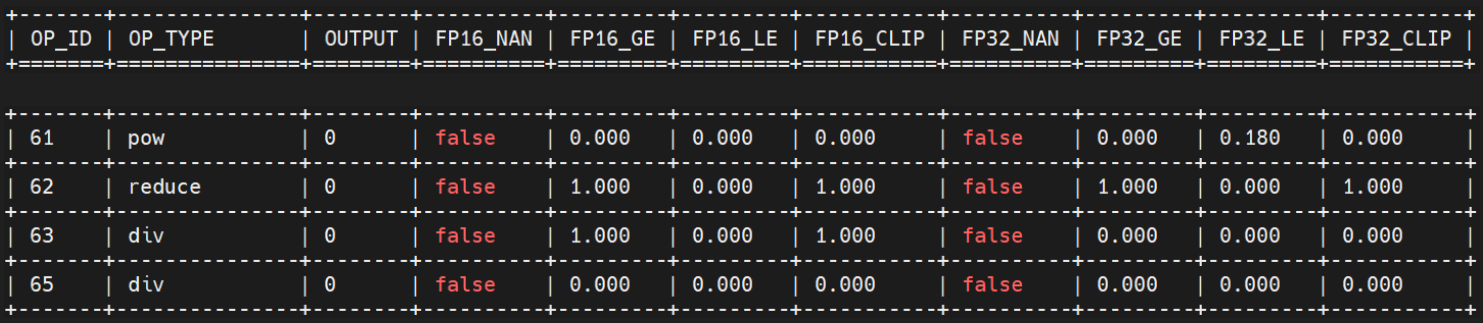
图 5.1.5 步骤2详细结果¶
步骤3. 将62 63设为fp32
topsideas gcu mix_precision --input_onnx lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx --manual --sample_dir ./lprnet-samples/ --workspace=./workspace --output_json result.json --mode=CALC --fp32_nodes 62 63
整网fp16 pass:

图 5.1.6 步骤3整网结果¶
步骤4. 关闭调试模式,产生可用于部署的executable
topsideas gcu mix_precision --input_onnx lprnet-pt-op13-fp32-N.onnx --manual --sample_dir ./lprnet-samples/ --workspace=./workspace --output_json result.json --mode=CALC --fp32_nodes 62 63 --finalize
RAW模式
上例中,CALC模式提供的信息已经足够判断哪些节点需要使用fp32,如果不够,可以用RAW模式,提供更多统计信息,如numpy allclose、cos similarity等。
json格式报表
每次执行后,除了控制台输出外,也会输出json格式报表。
CALC模式输出json格式:
{
"op_statistic": [{
"2": {
"id": 2,
"type": "conv_bias",
"outputs": [
{
"fp16_ge_ratio": 0.0,
"fp16_le_ratio": 0.7616068124771118,
"fp16_clip_ratio": 0.0,
"fp16_check_nan": false,
"fp32_ge_ratio": 0.0,
"fp32_le_ratio": 0.761599063873291,
"fp32_clip_ratio": 0.0,
"fp32_check_nan": false
}
]
},
// ......
}],
"output_files": {
"fp16_executable": "/path/to/workspace/fp16.executable",
"fp16_hlir": "/path/to/workspace/irdump/tops_ir_dump_xxxxxx.log",
"fp32_executable": "/path/to/workspace/fp32.executable",
"fp32_hlir": "/path/to/workspace/irdump/tops_ir_dump_xxxxxx.log"
},
"model_outputs": [{
"output": {
"fp16_golden": {
// ......
},
"fp32_golden": {
// ......
},
"fp16_fp32": {
// ......
}
}
}]
}
RAW模式输出json格式:
{
"op_statistic": [{
"2": {
"id": 2,
"type": "conv_bias",
"outputs": [
{
"fp16_element_count": 802816,
"fp16_nan_count": 0,
"fp32_element_count": 802816,
"fp32_nan_count": 0,
"numpy_allclose": "pass",
"exceed_tol_count": 0,
"cos_sim_value": 0.9999958276748657,
"norm_rel": 0.9999895095825195
}
]
},
// ......
}],
"output_files": {
"fp16_executable": "/path/to/workspace/fp16.executable",
"fp16_hlir": "/path/to/workspace/irdump/tops_ir_dump_xxxxxx.log",
"fp32_executable": "/path/to/workspace/fp32.executable",
"fp32_hlir": "/path/to/workspace/irdump/tops_ir_dump_xxxxxx.log"
},
"model_outputs": [{
"output": {
"fp16_golden": {
// ......
},
"fp32_golden": {
// ......
},
"fp16_fp32": {
// ......
}
}
}]
}
API¶
AutoMixPrecision¶
AutoMixPrecision是自动混精工具入口。
参数
argument |
type |
default |
|---|---|---|
input_onnx |
onnx.onnx_ml_pb2.ModelProto |
|
input_names |
List[str] |
|
input_shapes |
List[List[int]] |
|
min_shapes |
List[List[int]] |
None |
max_shapes |
List[List[int]] |
None |
构造示例
import onnx
from topsideas.gcu.mix_precision.auto_mix_precision import AutoMixPrecision
model = onnx.load('onnx_path')
tool = AutoMixPrecision(model, ['input_name'], [[shape_0,shape_1,shape_2,shape_3]])
AutoMixPrecision.run¶
参数
argument |
type |
default |
|---|---|---|
sample_inputs |
List[Any] |
|
sample_outputs |
List[Any] |
|
block_op_ids |
List[int] |
None |
rtol |
float |
1e-2 |
atol |
float |
1e-2 |
val_func |
Callable[[Any, Any], bool] |
None |
card_id |
int |
0 |
cluster_id |
int |
-1 |
resource_mode |
str |
None |
RETURN |
List[int] |
说明
sample_inputs: onnx模型输入样本,可以是多个样本。
sample_outputs: 对应每个输入样本的输出。
block_op_ids:哪些node必须使用fp32,默认不包含任何node。
rtol/atol:相对/绝对容忍度,如用户指定val_func,该项不起作用,否则用rtol和atol判断输出是否可接受。
val_func:可以是用户自定义评价函数,输入1:模型参考输出结果,输入2:当前混精输出结果,返回值为bool值,True表示结果可接受,False表示结果不可接受。函数体中可以对两个输入做任何后处理,用户可自行定义。
card_id:gcu card id。
cluster_id:gcu card cluster id。
resource_mode:TopsInference 编译选项,例如1c4s, 1c12s等。
返回值:fp32 id list,包含为满足混精精度需要设置为fp32的节点id。
使用示例
...
def post(res):
return res.astype(np.int32)
def val(cpu_out, gcu_out):
Tp = 0
Tn_1 = 0
Tn_2 = 0
for i, label in enumerate(gcu_out):
if len(label) != len(cpu_out[i]):
Tn_1 += 1
continue
if (np.asarray(gcu_out[i]) == np.asarray(label)).all():
Tp += 1
else:
Tn_2 += 1
Acc = Tp * 1.0 / (Tp + Tn_1 + Tn_2)
if Acc >= 0.9:
return True
else:
return False
def val_func(res0, res1):
cpu_out = post(res0[0])
gcu_out = post(res1[0])
return val(cpu_out, gcu_out)
tool = AutoMixPrecision(model, ['input_name'], [[shape_0,shape_1,shape_2,shape_3]])
tool.run(sample_inputs, sample_outputs, val_func=val_func)
...
AutoMixPrecision.finalize¶
参数
argument |
type |
default |
|---|---|---|
fp32_ids |
List[int] |
|
card_id |
int |
0 |
cluster_id |
int |
-1 |
resource_mode |
str |
None |
RETURN |
TopsInference.PyEngine |
使用示例
...
def post(res):
return res.astype(np.int32)
def val(cpu_out, gcu_out):
Tp = 0
Tn_1 = 0
Tn_2 = 0
for i, label in enumerate(gcu_out):
if len(label) != len(cpu_out[i]):
Tn_1 += 1
continue
if (np.asarray(gcu_out[i]) == np.asarray(label)).all():
Tp += 1
else:
Tn_2 += 1
Acc = Tp * 1.0 / (Tp + Tn_1 + Tn_2)
if Acc >= 0.9:
return True
else:
return False
def val_func(res0, res1):
cpu_out = post(res0[0])
gcu_out = post(res1[0])
return val(cpu_out, gcu_out)
tool = AutoMixPrecision(model, ['input_name'], [[shape_0,shape_1,shape_2,shape_3]])
fp32_ids = tool.run(sample_inputs, sample_outputs, val_func=val_func)
engine = tools.finalize(fp32_ids)