前言¶
目的¶
在 AI 的应用场景中,针对视频流进行 AI 处理是很常见的应用场景。由于使用 CPU 进行视频处理比较占用 CPU 资源,而且视频相关的原始数据如 YUV 文件等尺寸比较大,将这些文件从 CPU 传输到 AI 芯片比较耗时,因此在燧原 GCU3.0 的芯片中,燧原科技增加了专门处理视频编解码的 VCU IP,VCU IP 可以释放 CPU 的资源,同时数据在 GCU 内部流转也比较高效。
在视频编解码领域中,FFmpeg 是比较常见的视频编解码框架,因此燧原科技提供 FFmpeg 插件,用于在 FFmpeg 中使用 GCU 中的 VCU IP。
本用户手册默认读者已经具备相关的知识背景,如基本的视频编解码知识以及 FFmpeg 框架的使用方式,因此本手册并没有使用过多的篇幅用于介绍编解码和 FFmpeg 相关的知识,重点介绍了 GCU 中 VCU IP 相关的硬件架构以及支持的功能,读者通过阅读本手册,可以了解到 GCU 的 VCU 支持的功能,以及如何在 FFmpeg 中使能 GCU 的 VCU 功能。
VCU 硬件参数¶
GCU 中最小的解码单元为一个 VCU Core,多个 VCU Core 组成多个 VCU 设备,不同 VCU Core 支持的格式略有不同,对于同一个支持的格式,不同的 VCU Core 能力相同,解码能力以产品手册为准。
1 个 DIE 有 4 个 VCU 设备, 1 个 DIE 的目标最大路数为 128*1080p30FPS,目标最大 FPS 为 4*1080p960FPS。
值得注意的是,虽然 JPEG 支持 32K*32K 的分辨率,但是 FFmpeg 框架中本身有分辨率尺寸的限制,无法支持。FFmpeg 使用 INT_MAX 做限制,具体支持的最大分辨率根据不同平台而定。
解码器 Online 模块¶
解码器内部提供了额外的后处理模块,可以几乎不影响性能的完成相应的后处理。
Online 模块只能由 Codec 本身使用,无法独立使用,也无法变更 pipeline 的顺序(Crop 与 Rotation 不能同时使用)。
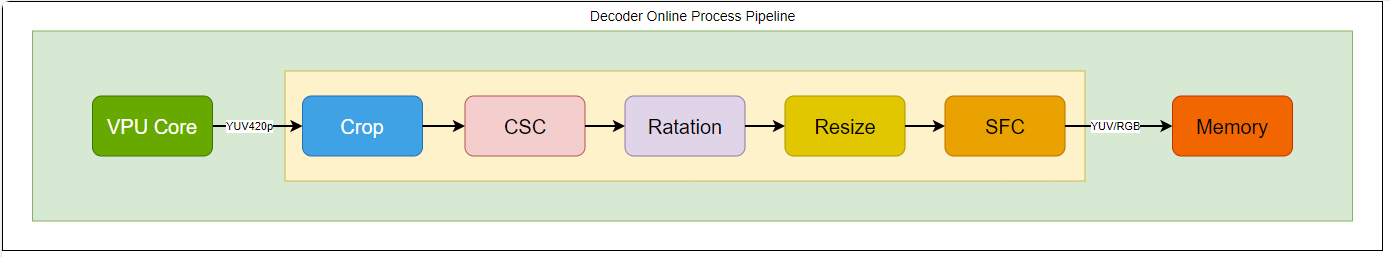
图 1 online-decoder¶
VCU 设备的选择¶
如同在软件架构示意图里看到的,多设备的调度是由用户来决策的。Codec 的设备节点在/dev 目录下,标准形式为/dev/gcuXvidY,其中X指的是卡号,Y指的是卡中的设备号,具体可用设备数量取决于在创建虚拟机时划入的设备数量。
Codec 格式与插件名称的对应关系¶
Codec 格式 |
插件名称 |
|---|---|
AV1 |
av1_topscodec |
HEVC (H.265) |
hevc_topscodec |
AVC (H.264) |
h264_topscodec |
AVS |
avs_topscodec |
AVS2 |
avs2_topscodec |
VP8 |
vp8_topscodec |
VP9 |
vp9_topscodec |
JPEG |
mjpeg_topscodec |
VC‑1 |
vc1_topscodec |
MPEG4 |
mpeg4_topscodec |
MPEG2 |
mpeg2_topscodec |
H.263 |
h263_topscodec |
RealVideo |
N/A |
支持的参数¶
FFmpg_GCU 支持的参数
参数 |
使用 |
备注 |
|---|---|---|
vcodec |
-vcodec h264_topscodec |
参数见上表插件名称 |
card_id |
-card_id 0 |
范围 0~8 |
device_id |
-device_id 0 |
范围 0-4 |
hw_id |
-hw_id 15 |
default 15 |
sf |
-sf 0 |
0/1 |
out_port_num |
-out_port_num 15 |
default 8 |
zero_copy |
-zero_copy 0 |
1/0 |
output_pixfmt |
-output_pixfmt nv12 |
参数见下表 output_pixfmt |
output_colorspace |
-output_colorspace bt2020 |
参数见下表 output_colorspace |
enable_crop |
-enable_crop 1 |
0/1 |
crop_top |
-crop_top x |
|
crop_bottom |
-crop_bottom x |
|
crop_left |
-crop_left x |
|
crop_right |
-crop_right x |
|
enable_rotation |
-enable_rotation 1 |
0/1 |
rotation |
-rotation 90 |
90/180/270 |
enable_resize |
-enable_resize 0 |
0/1 |
resize_w |
-resize_w x |
|
resize_h |
-resize_h x |
|
resize_m |
-resize_m 0 |
0/1 |
sfo |
-sfo 0 |
0-INT_MAX |
idr |
-idr 0 |
0/1t |
参数 resize_m 指 downscale 的模式,0-Bilinear, 1-Nearest。
参数 sfo 指抽帧间隔。
参数 idr 指只输出 IDR 关键帧。
参数 sf 指解码优化参数,单路解码设置为 0,多路解码设置为 1。
支持的输出格式 output_pixfmt
index |
avformat |
str |
|---|---|---|
1 |
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P |
yuv420p |
2 |
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24 |
rgb24 |
3 |
AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24 |
bgr24 |
4 |
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24P |
rgb24p |
5 |
AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24P |
bgr24p |
6 |
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P |
yuv444p |
7 |
AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8 |
gray8 |
8 |
AV_PIX_FMT_NV12 |
nv12 |
9 |
AV_PIX_FMT_NV21 |
nv21 |
10 |
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P10LE |
yuv444ple |
11 |
AV_PIX_FMT_P010LE(topscodec p010) |
p010 |
12 |
AV_PIX_FMT_P010BE(topscodec p010le) |
p010le |
13 |
AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY10LE |
gray10 |
提示说明:ffmpeg topscodec online 8bit->10bit 的转换:
字节左移(<<) 2bit,然后补 0,如果为小端,左移后的高位在大地址,例如某一个字节为 0xeb(1110 1011)转换后就成为了 0xac03(1010 1100 0000 0011),以此类推。
yuv420p->gray10 提取 Y 分量,将 Y 分量中的每一个字节(8bit),然后按照上述操作每一个字节。
yuv420p->p010le 重新排列 YCrCb 为 YYY…CrCbCrCbCrCb…,然后按照上述操作每一个字节。
单纯的增加一个 0x00 的字节就可以了,比如原始字节为 0xeb(1110 1011),那么转到 10bit 后就成了 0x00 eb 或者 0xeb 00。
yuv420p->p010 重新排列 YCrCb 为 YYY…CrCbCrCbCrCb…,然后按照上述操作每一个字节。
yuv420p->yuv444p10,插值 CrCb 分量,最后为 YYY…CrCrCr…CbCbCb…,然后按照上述方式操作每一个字节。
支持的颜色空间 output_colorspace
index |
colorspace |
|---|---|
1 |
bt601 |
2 |
bt601f |
3 |
bt709 |
4 |
bt709f |
5 |
bt2020 |
6 |
bt2020f |
安装使用¶
FFmpeg_GCU 依赖 TopsRider 软件栈,需要同时安装 TopsRider 软件栈和 FFmpeg_GCU,然后进行相关的使用。
FFmpeg_GCU 采用源码 release 的方式,目前源代码直接 release 在安装包中,后期会提供开源网站的链接供客户下载,源代码 release 分两部分:
FFmpeg_GCU 依赖的头文件(实现底层库的动态加载)。
FFmpeg_GCU 插件本身。
安装 FFmpeg_GCU 的 deb 文件后,可以拿到预编译好的可执行文件和源代码,在头文件目录运行 make 命令即可把头文件安装到系统目录,然后在插件目录进行 FFmpeg 的编译,这里假定用户具备了 FFmpeg 编译的相关知识背景,因此没做详细介绍。
应用举例¶
FFmpeg 命令行¶
FFmpeg 命令行解码的设置(为了防止 ffmpeg 根据 pts 进行抽帧和插帧,增加-vsync 0,另外-hide_banner 是隐藏编译说明信息,-v trace 是打开 log,可以根据实际情况添加或者删除)。
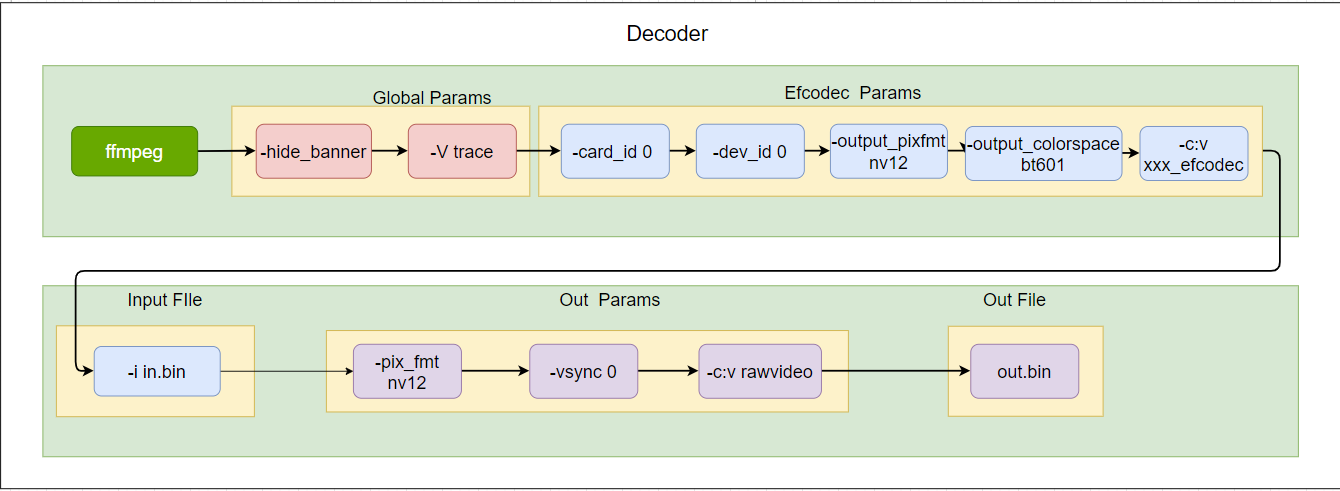
图 2 ffmpeg-cmd2¶
使用第 0 张卡上的第 0 个 dev 的 h264_topscodec 解码器,解码 in.bin 并输出到 out.bin,默认输出格式为 yuv420p
ffmpeg -hide_banner -v trace -card_id 0 -device_id 0 -c:v h264_topscodec -i in.bin -c:v rawvideo -vsync 0 out.bin
使用第 0 张卡上的第 0 个 dev 的 h264_topscodec 解码器,并且使用 online 中的 csc 功能,将 in.bin 解码后的 yuv420p 转换为 Output Pixel 后输出到 out.bin
ffmpeg -hide_banner -v trace -card_id 0 -device_id 0 -output_pixfmt nv12 -output_colorspace bt601 -c:v h264_topscodec -i in.bin -pix_fmt nv12 -c:v rawvideo -vsync 0 out.bin
FFmpeg C API¶
下面代码展示了 FFmpeg 调用 efcpdec 的关键 api 使用。
/*
本例展示了如何在ffmpeg api中调用到topscodec解码器插件
*/
int main(int argc, char** argv){
int ret;
AVFormatContext *input_ctx = NULL;
AVStream *video = NULL;
AVCodec *decoder = NULL;
AVCodecContext *decode_ctx = NULL;
AVDictionary *dec_opts = NULL;
char *inf_file = "test.264"
if (avformat_open_input(&input_ctx, in_file, NULL, NULL) != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open input file '%s'\n", in_file);
return -1;
}
if (avformat_find_stream_info(input_ctx, NULL) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find input stream information.\n");
return -1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < input_ctx->nb_streams; i++) {
if (input_ctx->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type ==
AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
video = input_ctx->streams[i];
video_stream = i;
break;
}
}
if (NULL == video) {
fprintf(stderr, "video stream is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
switch(video->codecpar->codec_id) {
case AV_CODEC_ID_H264:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("hevc_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_VP8:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("vp8_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_VP9:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("vp9_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEG:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("mjpeg_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_H263:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h263_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("mpeg2_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("mpeg4_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_VC1:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("vc1_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_CAVS:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("avs_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_AVS2:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("avs2_topscodec"); break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_AV1:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("av1_topscodec"); break;
default:
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder(video->codecpar->codec_id); break;
}
decode_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(decoder);
av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "device_id", dev_id, 0);
av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "output_pixfmt", out_fmt, 0);
/*+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*/
// examples for other options:
// 1. set the out_port_num
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "out_port_num", "6", 0);
// 2. set the zero_copy
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "zero_copy", "1", 0);
// 3. set the rotation (only support orientation,90/180/270)
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "enable_rotation", "1", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "rotation", "90", 0);
// 4. set the crop
// (w * h)
// (0,0)-------------------------------------------+
// + | | +
// + crop_top | +
// + | | +
// +---crop_left--+ | +
// + | +
// + crop_bottom +
// + | +
// +--------------crop_right-----+ +
// + +
// +-------------------------------------------(w,h)
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "enable_crop", "1", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "crop_left", "20", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "crop_top", "20", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "crop_right", "1900", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "crop_bottom", "1060", 0);
// 5. set the resize (0-Bilinear, 1-Nearest)
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "enable_resize", "1", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "resize_w", "640", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "resize_h", "360", 0);
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "resize_m", "0", 0);
// 6. set the idr_only (only decode the IDR frame)
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "idr", "1", 0);
// 7. set the interval (decode the frame every interval)
// if interval is 2, x00x00x00x00x.., x is the frame, 0 is the discard frame
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "sfo", "2", 0);
// 8. set the balance rate (0-300)
// recommend value:single core:0, multi-core:5
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "sf", "5", 0);
// 9. set the output_colorspace
// support bt601, bt709, bt2020, bt601f, bt709f, bt2020f
// av_dict_set(&dec_opts, "output_colorspace", "bt709", 0);
/*+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*/
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(decode_ctx, decoder, &dec_opts)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open codec for stream #%d\n",
video_stream);
return -1;
}
/*fmt_Ctx为 demux部分,本示例代码中略去*/
while(1) {
ret = av_read_frame(fmt_ctx, &packet);
if ((ret = av_read_frame(input_ctx, &packet)) < 0)
break;
ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, &packet);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(dec_ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"send pkt failed, ret(%d), %s, %d\n",
ret, __FILE__, __LINE__);
goto fail;
}
while (ret >= 0 || eos) {
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, p_frame);
if (ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
av_log(g_dec_ctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "dec receive eos\n");
av_frame_unref(p_frame);
av_frame_free(&p_frame);
return 0;
} else if (ret == 0) {
save_yuv_file(dec_ctx, p_frame);
av_frame_unref(p_frame);
} else if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
av_log(dec_ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "receive frame failed\n");
goto fail;
}
}
av_packet_unref(&packet);
}
fail:
avcodec_free_context(&decode_ctx);
return 0;
}
OpenCV C++ API¶
OpenCV 版本需要 3.4.2 及以上
在 OpenCV 中使用 FFmpeg 功能的时候,需要先安装 FFmpeg 到/usr/local 目录下,一般官方默认的安装包中是带有 FFmpeg 支持的,所以只要把 FFmpeg 安装后,在 OpenCV 中就可以直接调用 FFmpeg 的 API。
如果报错可以尝试重新编译,具体编译方式参考下面命令:
cd OpenCV
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D OPENCV_GENERATE_PKGCONFIG=YES ..
make -j4
make install
采用 OpenCV 的时候需要注意以下几点:
1)不要使用 FFmpeg topscodec 中的任何 online 参数,OpenCV 会默认采用 FFmpegg 的相关 fileter 进行 yuv2bgr 和 resize 的操作。
2)OpenCV 会将 FFmpeg topscodec 解码后的数据自动进行 YUV2BGR 转换,并且自动进行设备到主机之间数据的拷贝,这个操作极为耗时。
OpenCV 提供了VideoCapture类来提供获取视频帧的功能,其中包括视频文件的解码功能,详细的 API 介绍可以参考 OpenCV 社区提供的文档。
https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.2/d8/dfe/classcv_1_1VideoCapture.html
OpenCV 调用 FFmpeg topscodec 相关代码片段如下:
/*
本案例主要介绍了,如何使用Opencv api 去调用ffmpeg topscodec 插件的方法
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/cvdef.h"
#include "opencv2/core/utils/logger.hpp"
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
printf(
"usage: %s input_file only support h264\n"
"API example program to show how to read"
"frames from an input file.\n"
"This program reads frames from a file,"
"decodes them, and writes decoded\n"
"video frames to a jpeg file\n",
argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
cv::utils::logging::setLogLevel(cv::utils::logging::LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG);
//OpenCV的Mat数据结构,用于存储获取到的数据帧
cv::VideoCapture capture;
//OpenCV的Mat数据结构,用于存储获取到的数据帧
cv::Mat frame;
/*
* 设置环境变量 OPENCV_FFMPEG_CAPTURE_OPTIONS=video_codec;h264_topscodec
* 上面设置的含义为:ffmpeg的解码器选择h264_topscodec,
* 类似于ffmpeg中的-vcodec h264_topscodec
* 如果设置了多个option参数,可以通过'|'来分割:
* OPENCV_FFMPEG_CAPTURE_OPTIONS=video_codec;
* h264_topscodec|device_id;1|zero_copy;0
* 上述设置相当于ffmpeg中的ffmpeg -zero_copy 0 -device_id 1 -vcodec
* h264_topscodec -i test.264 xxx
* 注意一点的是,上述全局变量的设置只针对Opencv3.4.2及以上的版本
* Opencv3.4.1及以下的版本如果要使用ffmpeg指定的解码器,
* 需要在configure ffmpeg的时候只打开你需要的那个 解码器就可以了。
*/
putenv("OPENCV_FFMPEG_CAPTURE_OPTIONS=video_codec;h264_topscodec");
/*
*设置ffmpeg中的log levle
*/
putenv("OPENCV_FFMPEG_LOGLEVEL=48");
putenv("OPENCV_FFMPEG_DEBUG=1");
char *infile = argv[1];
/*
*打开文件,值得要注意的是,TopsVideo通过FFmpeg提供解码的后端支持,
*因此一定要增加cv::CAP_FFMPEG的选择
*/
if (!capture.open(infile, cv::CAP_FFMPEG)) {
printf("can not open infile %s ...\n", infile);
return -1;
}
int num = 0;
while (capture.read(frame)) {//读取解码得到的视频帧
if (frame.empty())
break;
//后续视频帧的处理,跟OpenCV的Mat的操作,完全一致
num++;
printf("frame=%d\n", num);
std::string name = "save_" + std::to_string(num) + ".jpg";
imwrite(name, frame);
}
printf("end of stream,num=%d!\n", num);
capture.release();
return 0;
}
Py-AV Python API¶
PyAV: https://github.com/PyAV-Org/PyAV
PyAV 提供了一套 python 接口来调用 FFmpeg api 接口,下面主要介绍如何通过 PyAV 调用到 FFmpeg_GCU。因为这里使用我们自己的芯片做加速,所以首先安装我们的 FFmpeg,然后安装在/usr/local 目录下。
安装 Py-AV,选择不安装官方的 FFmpeg,pip install av --no-binary av
Parser + decoder¶
下面的案例是通过调用 codec 内部内置的 parser 来解析 h264packet,这里只支持 annexb 格式,不支持 avcc 格式。
import os
import subprocess
import logging
import time
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.getLogger('libav').setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
import av
import av.datasets
# We want an H.264 stream in the Annex B byte-stream format.
# We haven't exposed bitstream filters yet, so we're gonna use the `FFmpeg` CLI.
h264_path = "libx264_640x360_baseline_5_frames.h264"
if not os.path.exists(h264_path):
subprocess.check_call(
[
"FFmpeg",
"-i",
av.datasets.curated("zzsin_1920x1080_60fps_60s.mp4"),
"-vcodec",
"copy",
"-an",
"-bsf:v",
"h264_mp4toannexb",
h264_path,
]
)
fh = open(h264_path, "rb")
#此处选择h264_topscodec 作为解码器
codec = av.CodecContext.create("h264_topscodec", "r")
#设置参数
codec.options={"card_id":"0","dev_id":"1","hw_id":"15"}
#打开解码器
codec.open()
print(codec.name)
first= True
count=0
while True:
chunk = fh.read(1 << 16)
packets = codec.parse(chunk)
print("Parsed {} packets from {} bytes:".format(len(packets), len(chunk)))
for packet in packets:
print(" ", packet)
frames = codec.decode(packet)
if first:
time.sleep(2)
first=False
for frame in frames:
print(" ", frame)
count+=1
print('--count:%d--'%count)
frame.to_image().save("night-sky.{:04d}.jpg".format(count),quality=80,)
# We wait until the end to bail so that the last empty `buf` flushes
# the parser.
if not chunk:
break
p=av.Packet(None)
print("send eos:", p)
frames = codec.decode(p)
for frame in frames:
print(" ", frame)
count+=1
print('--count:%d--'%count)
frame.to_image().save("night-sky.{:04d}.jpg".format(count),quality=80,)
codec.close()
fh.close()
print('all count:%d'%count)
demuxer1 + decoder¶
这个案例要注意一点,它是无法通过参数设置调用到 FFmpeg_GCU 解码器中的解码器。如果非要用,只能编译 FFmpeg_GCU 的时候关闭除了 topscodec 外的所有解码器
import time
import av
import av.datasets
container = av.open('ocr_400_400_5_frames.mp4')
first=True
count=0
start_time = time.time()
for packet in container.demux():
print(packet)
for frame in packet.decode():
print(frame)
count+=1
print('---frame:%d---'%count)
if first:
time.sleep(2)
first=False
auto_time = time.time() - start_time
container.close()
print('all frame:%d',count)
demuxer2 + decoder¶
这个案例是采用 demuxer+codec decoder 的案例,为什么不直接使用 demux 中自带的 decoder 呢?这是因为其无法通过设置来选择解码器。所以我们不得不采用这种曲折迂回的办法来进行解码。
import os
import subprocess
import logging
import time
import av
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.getLogger('libav').setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
h264_path = "ocr_400_400_5_frames.mp4"
container = av.open(h264_path,options={"vsync":"0"})
in_stream = container.streams.video[0]
codec = av.CodecContext.create("h264_topscodec", "r")
codec.options={"card_id":"0","device_id":"0"}
codec.open()
print(codec.name)
# print(codec.extradata_size)
first=True
num = 0
for packet in container.demux(in_stream):
print('----packet---')
packet.dts =0
packet.pts = 0
print(" ", packet)
#这里一定要注意将demux中codec的extradata赋值到这里打开的codec.extradata中
codec.extradata =in_stream.codec_context.extradata
frames = codec.decode(packet)
print('---after decode---')
if first:
time.sleep(2)#第一次等待2s,等待解码器初始化准备好
first=False
for frame in frames:
print(" ", frame)
num+=1
print('-----frame:%d-----'%num)
print('all:%d'%num)
codec.close()
input_.close()